Why there is no review process followed in fake/bogus journals
Why there is no review process followed in fake/bogus journals
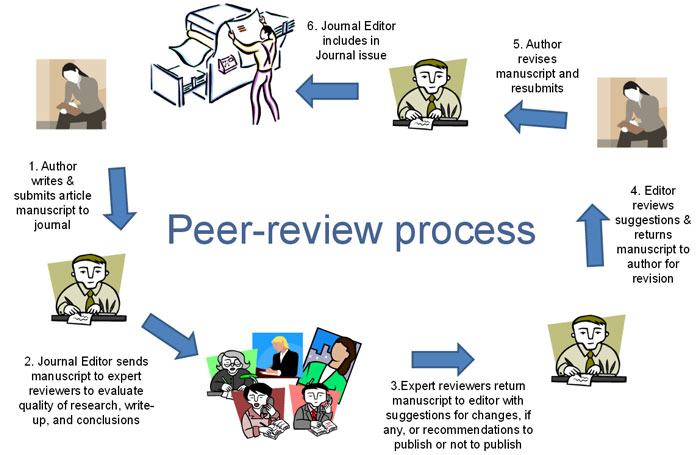
(Image credits: Actual peer-review process https://www.openacessjournal.com//assets/blog/What-is-peer-review.jpg)
Irrespective of reviewers and editorial members' knowledge, publisher publishes the contents submitted by authors. They are using copyright form as a weapon based on that publisher make authors completely responsible for their contents.
The following are some of the points due to this there is no rigorous review process followed by fake/bogus journals.
Profit Motive: Fake journals are primarily motivated by financial gain rather than the advancement of knowledge. They often charge authors publication fees without providing legitimate editorial and peer review services. By avoiding the costs associated with rigorous peer review, they maximize their profits.
Lack of Editorial Oversight: These journals typically lack a qualified editorial board or experienced editors. This absence of expertise can lead to a lack of quality control and rigorous review processes.
Rapid Publication: Fake journals often promise rapid publication of submitted manuscripts, sometimes within a few days or weeks. This attracts authors who want to publish their work quickly but may not realize that proper peer review and editing are essential for maintaining research quality.
Minimal or No Peer Review: In some cases, fake journals claim to conduct peer review but do not follow established scholarly standards. They may simply accept articles without a thorough review or assign reviews to unqualified individuals.
Low or No Standards: Fake journals typically do not adhere to the high academic and ethical standards that reputable journals follow. This can include accepting plagiarized content, poorly written papers, or articles that lack scientific rigor.
Lack of Transparency: These journals often do not provide transparent information about their editorial processes, peer review procedures, or publishing fees. Authors and readers may not have access to information about the journal's practices and policies.
Inadequate or Falsified Indexing: Some fake journals falsely claim to be indexed in well-known databases or directories, which can mislead authors and readers into thinking they are reputable.
Predatory Practices: Fake journals may use deceptive tactics to solicit submissions, such as sending spam emails to researchers or falsely claiming to be associated with legitimate academic institutions.
Limited Accountability: Fake journals often operate with little or no oversight, making it challenging to hold them accountable for unethical practices.
Thanks,
Team - JournalGuardians

Comments
Post a Comment